 |
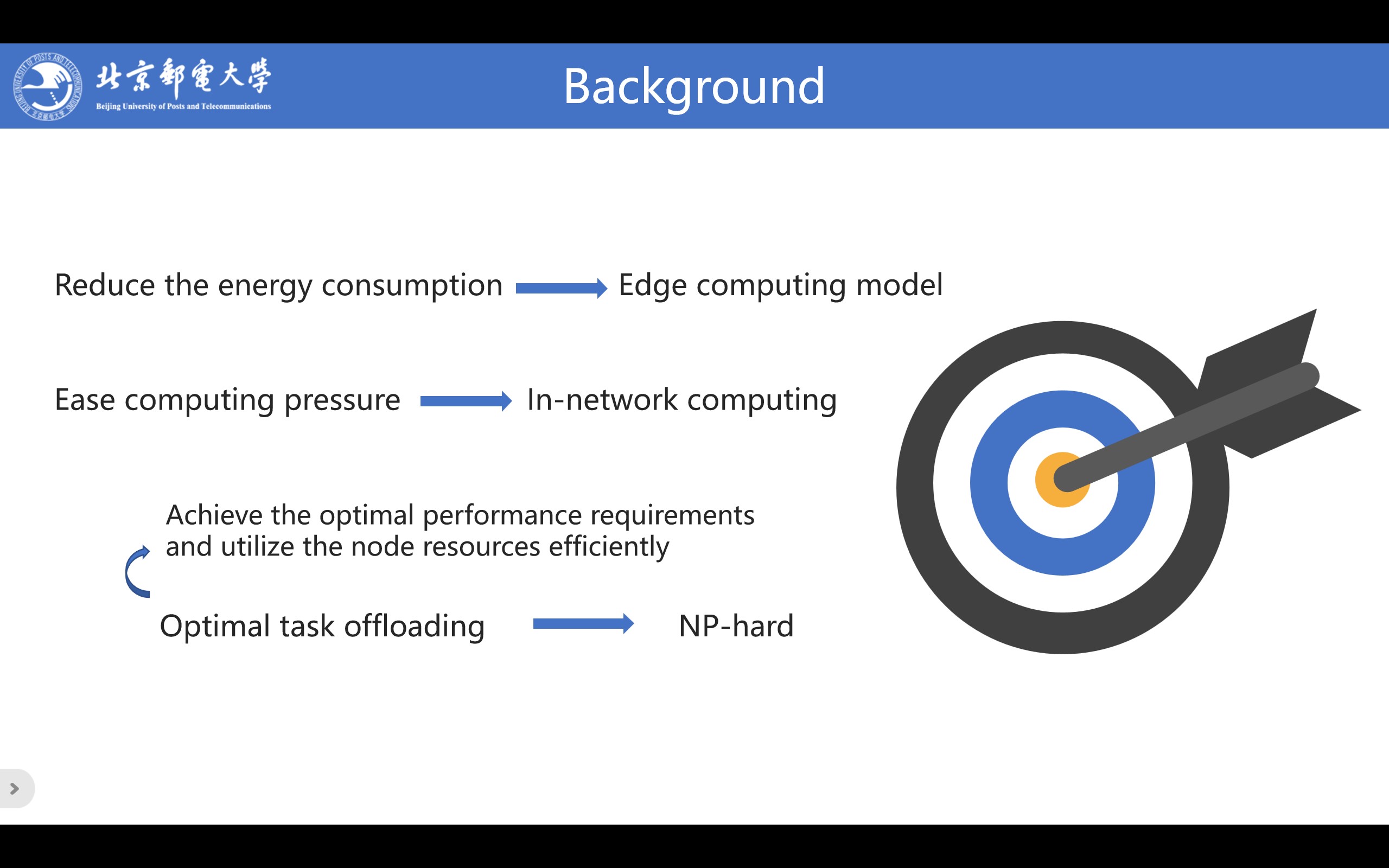
In order to reduce energy consumption of data centers, the industry proposes edge computing model. By offloading some computing tasks to edge devices, cloud servers and user devices reduce power consumption. The emergence of edge computing technology means that the traditional CPU-centric computing model begins to shift to data-centric computing.
In order to further ease the computing pressure in the cloud, the industry puts forward the in-network computing model. In-network computing is a new computing model that schedules processing tasks at the application layer to the network data plane. By offloading computing tasks at the user end to network nodes with computing power, traffic is forwarded and processed at the same time. This means that, without increasing the number of network devices, idle computing power of network devices can be fully utilized to complete some data processing, reduce bandwidth transmission load on the network, and share the processing and computing pressure of the cloud. The advent of network-based computing has changed TCP/IP networks, making them no longer conduits of data that are not aware of applications.
Optimal task offloading is not only to achieve the optimal performance requirements of running applications, but also to efficiently utilize the node resources in the network. Therefore, task offloading is clearly a multi-objective optimization problem, which is NP-hard. |
 IEEE/ICACT20230136 Slide.03
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230136 Slide.03
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 
 IEEE/ICACT20230136 Slide.03
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230136 Slide.03
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 