 |
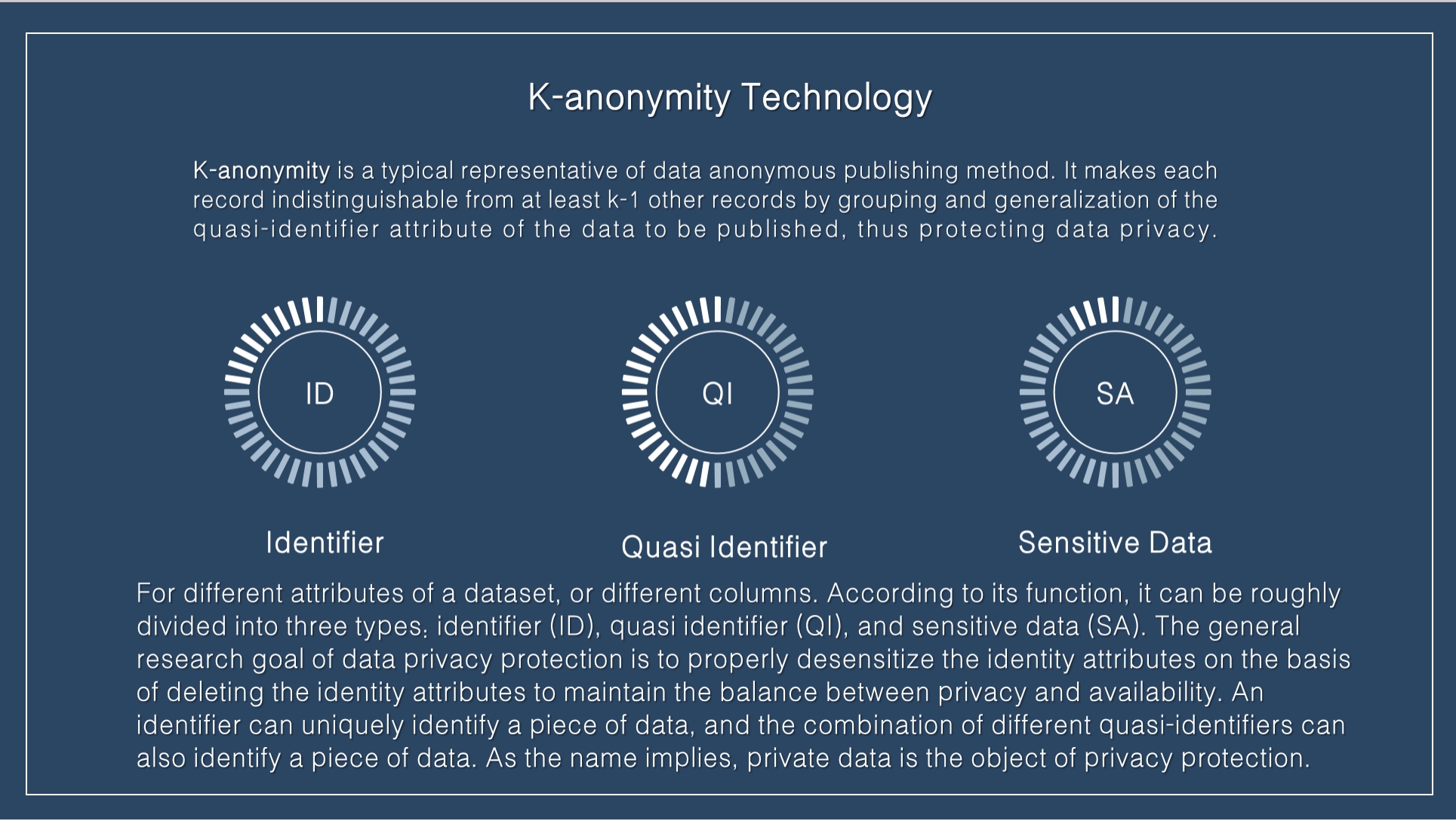
K-anonymity is a typical representative of data anonymous publishing method. It makes each record indistinguishable from at least k-1 other records by grouping and generalization of the quasi-identifier attribute of the data to be published, thus protecting data privacy. For different attributes of a dataset, or different columns. According to its function, it can be roughly divided into three types: identifier (ID), quasi identifier (QI), and sensitive data (SA). The general research goal of data privacy protection is to properly desensitize the identity attributes on the basis of deleting the identity attributes to maintain the balance between privacy and availability. An identifier can uniquely identify a piece of data, and the combination of different quasi-identifiers can also identify a piece of data. As the name implies, private data is the object of privacy protection.
The first step of k-anonymous data anonymity is to delete any explicit identifier that can directly define personal identity. Then, through the generalization technology, each record in the published data set cannot be distinguished from the k-1 record set that shares the same quasi-identifier value. These values are called "equivalent classes". K-anonymity technology can guarantee the following three points:
(1) Resist member inference attacks, and attackers cannot determine whether a target person is in the public data
(2) Sensitive information protection, given that an attacker cannot confirm whether he has a sensitive attribute
(3) Against reverse analysis attacks, attackers can't confirm who a piece of data corresponds to |
 IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.04
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.04
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 
 IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.04
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.04
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 