 |
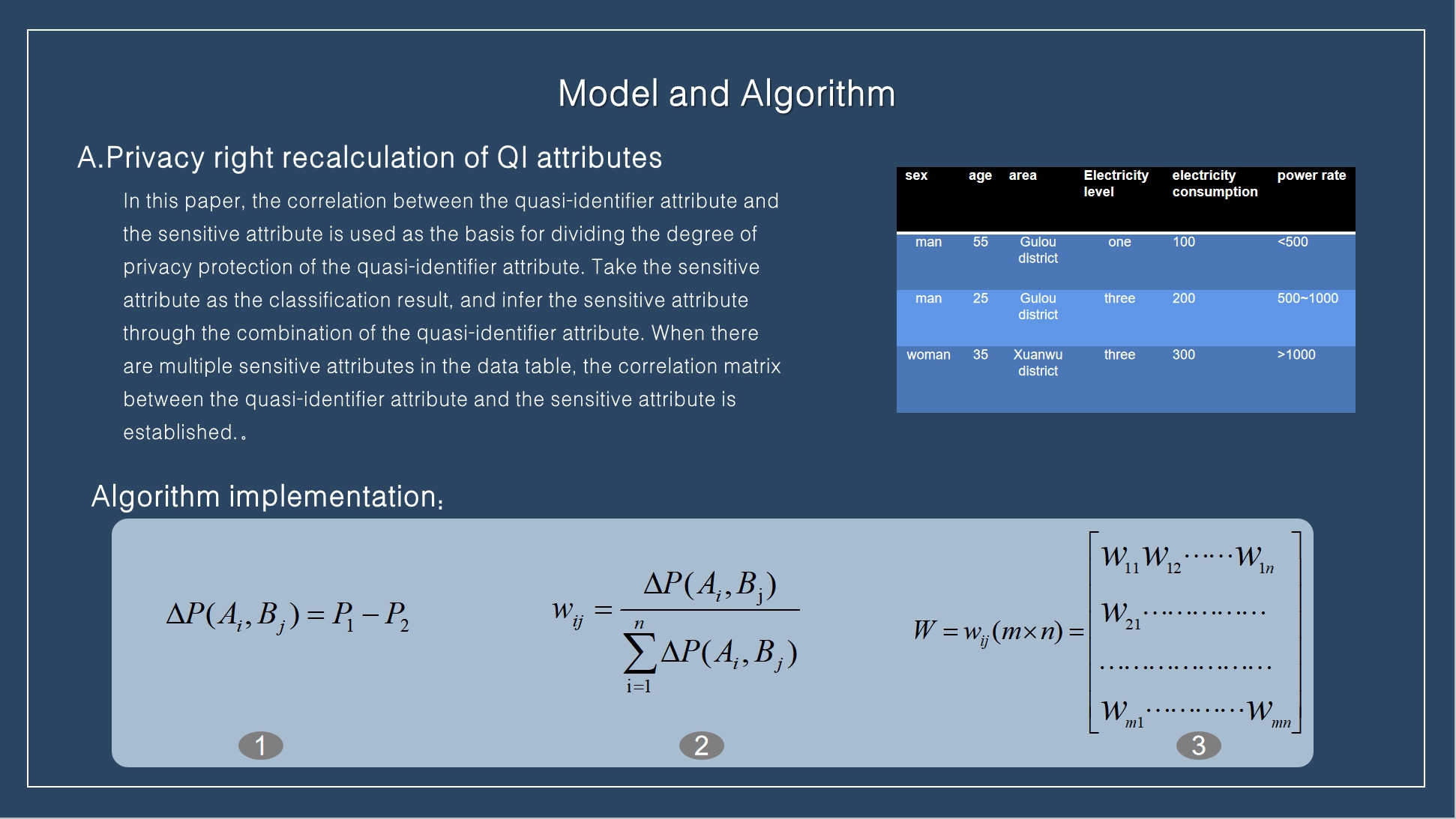
We take the correlation between the quasi-identifier attribute and the sensitive attribute as the basis for dividing the degree of privacy protection of the quasi-identifier attribute.
First, the sensitivity of data field attributes is predicted, and the impact of each attribute of data on sensitive attributes is calculated. Suppose a piece of data has n quasi-identifier QI attributes (A1, A2,..., An) and m sensitive attributes (B1, B2,..., Bm). First, calculate the average accuracy rate P1 of predicting sensitive attribute B1 through n QI attributes, and then calculate the average accuracy rate P2 of predicting sensitive attribute with the remaining n-1 QI attributes after deleting the attribute. The difference between the two indicates the impact of the attribute on the prediction of sensitive attribute. The greater the difference, the greater the impact.
Therefore, we can also express the sensitivity of the QI attribute to the sensitive attribute, namely (1). After calculating the sensitivity of n QI attributes to sensitive attribute Bj in turn, normalize them and calculate the privacy weight of each QI attribute, namely (2). After forecasting m sensitive attributes (B1, B2,..., Bm), all sensitivity components of QI attributes and sensitive attributes are obtained Ąż N-type privacy weight matrix, i.e. (3) |
 IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.07
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.07
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 
 IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.07
[Big Slide]
IEEE/ICACT20230212 Slide.07
[Big Slide]
 Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 