 |
Now we introduce our network£ºDenoising Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN).
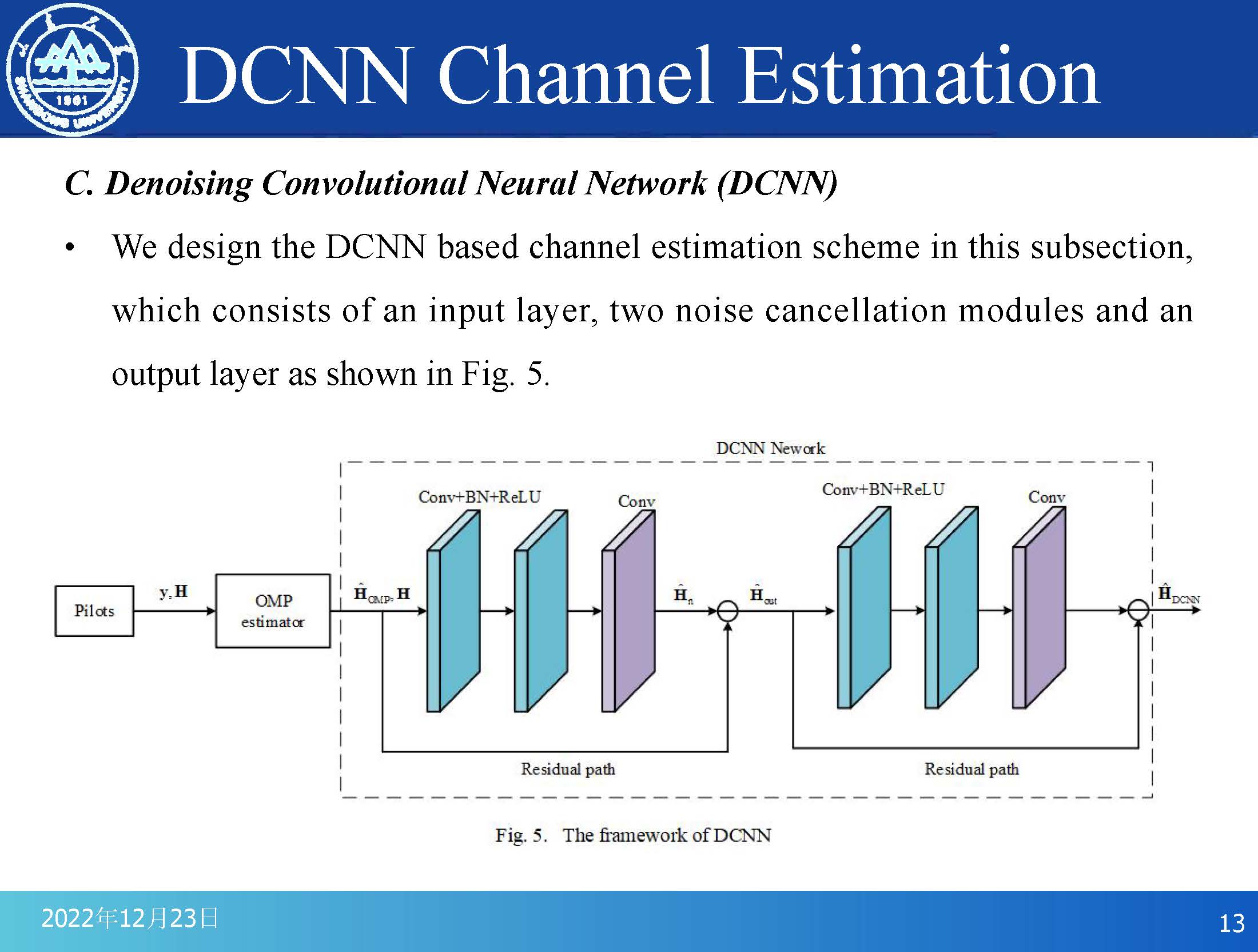
We design the DCNN based channel estimation scheme in this subsection,
which consists of an input layer, two noise cancellation modules and an
output layer as shown in Fig. 5.
Each noise cancellation module has a residual path and three convolutional layers of 3¡¿3 size, and the expansion dilation rates of these three convolutional layers are set to be 1, 2, and 5, respectively. First, the pre-estimated channel matrix HOMP obtained by the OMP algorithm is taken as the input of DCNN, and the real channel matrix H is used as the label. Through the first noise cancellation module, the DCNN distinguishes the difference between HOMP and H to achieve the extraction of the noise matrix Hn. Subsequently, the channel matrix Hout from the output layer of the first noise cancellation module is obtained by subtracting Hn from HOMP through the residual path. Finally, Hout is used as the input of the second noise cancellation module, and the actual channel matrix H is also set as the label, and the above operation is repeated to obtain the final channel estimation matrix HDCNN of DCNN.
The above channel estimation can eliminate the noise interference and achieve better accuracy. |
 IEEE/ICACT20230246 Slide.13
[Big Slide]
[YouTube]
IEEE/ICACT20230246 Slide.13
[Big Slide]
[YouTube]  Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 
 IEEE/ICACT20230246 Slide.13
[Big Slide]
[YouTube]
IEEE/ICACT20230246 Slide.13
[Big Slide]
[YouTube]  Oral Presentation
Oral Presentation 